Description
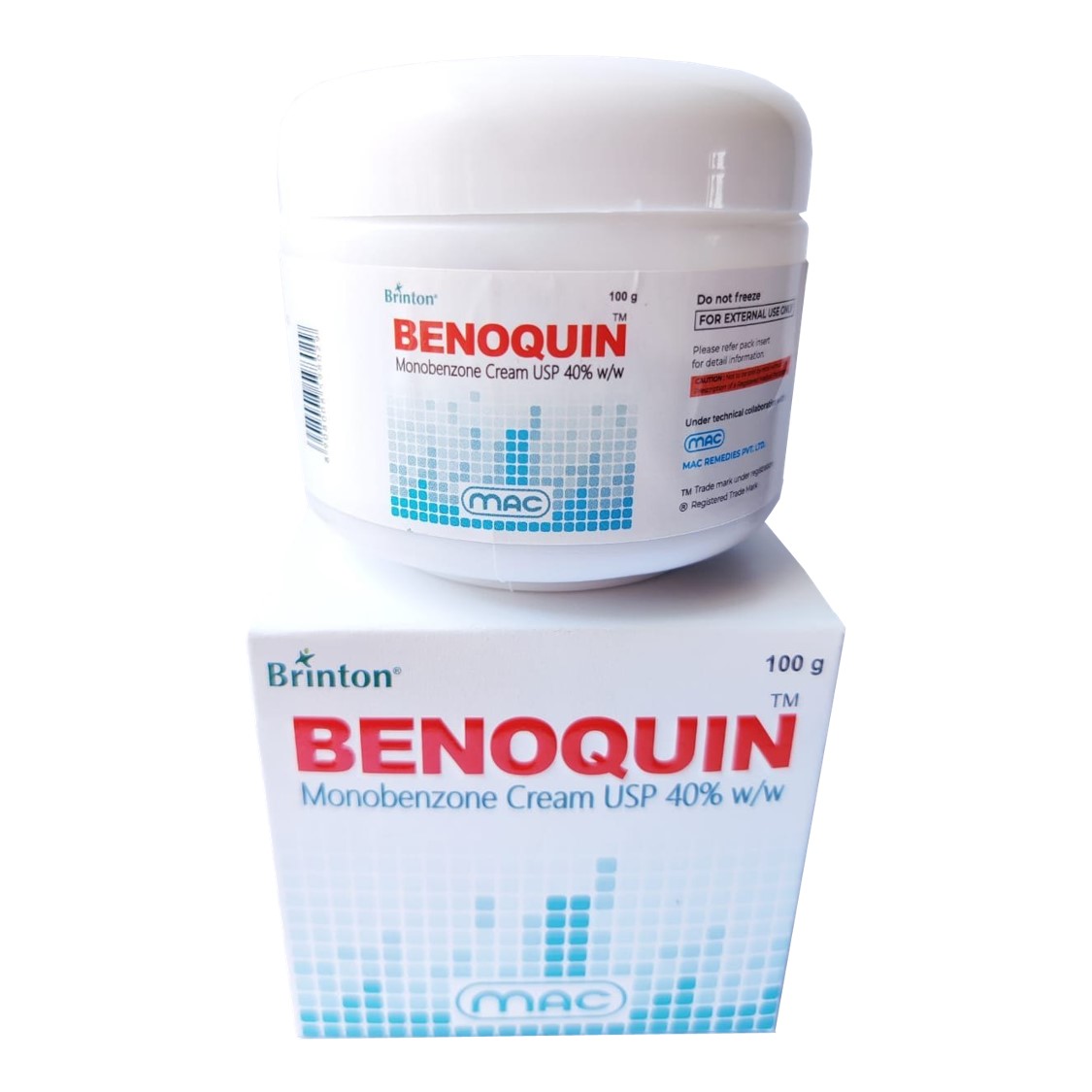
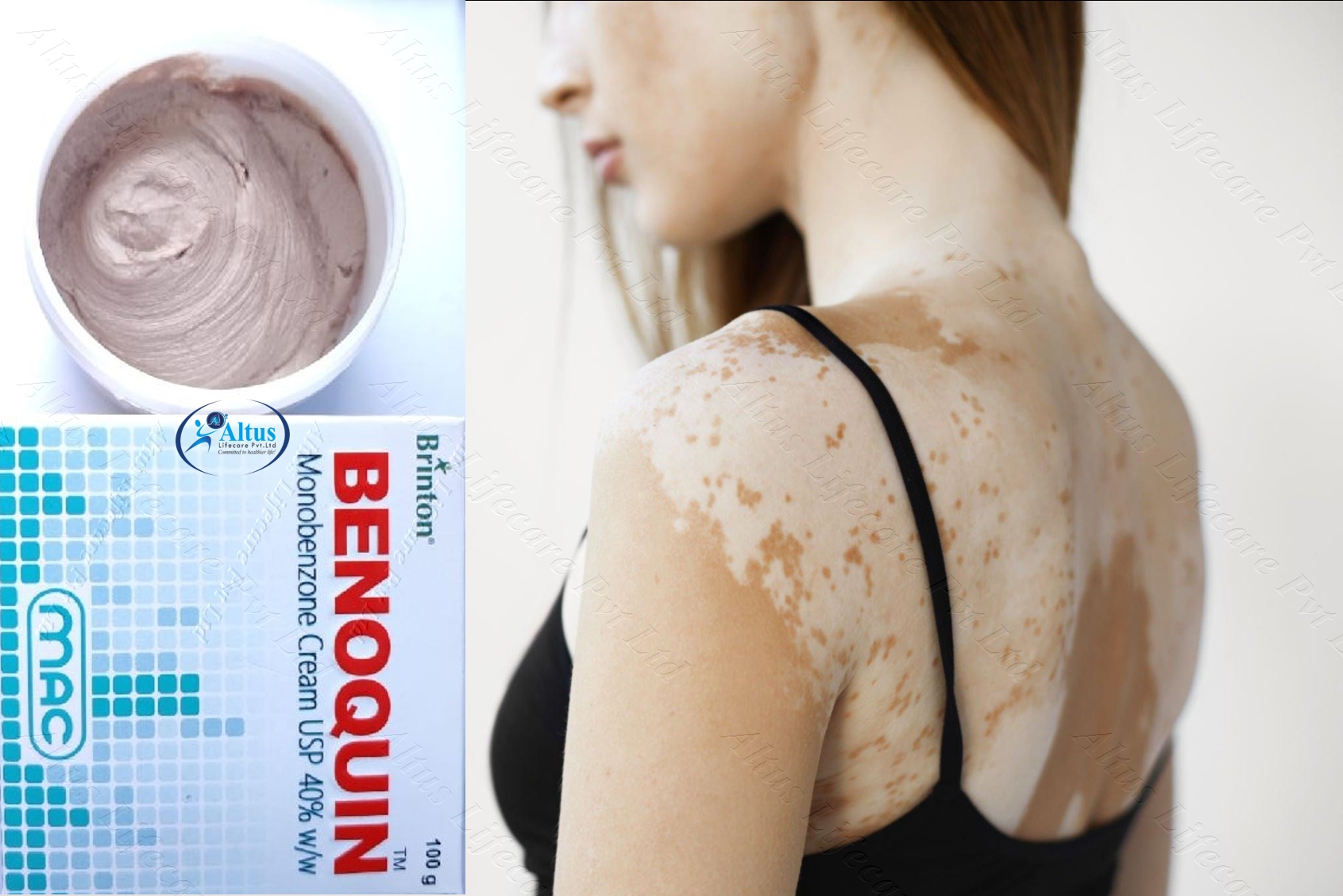
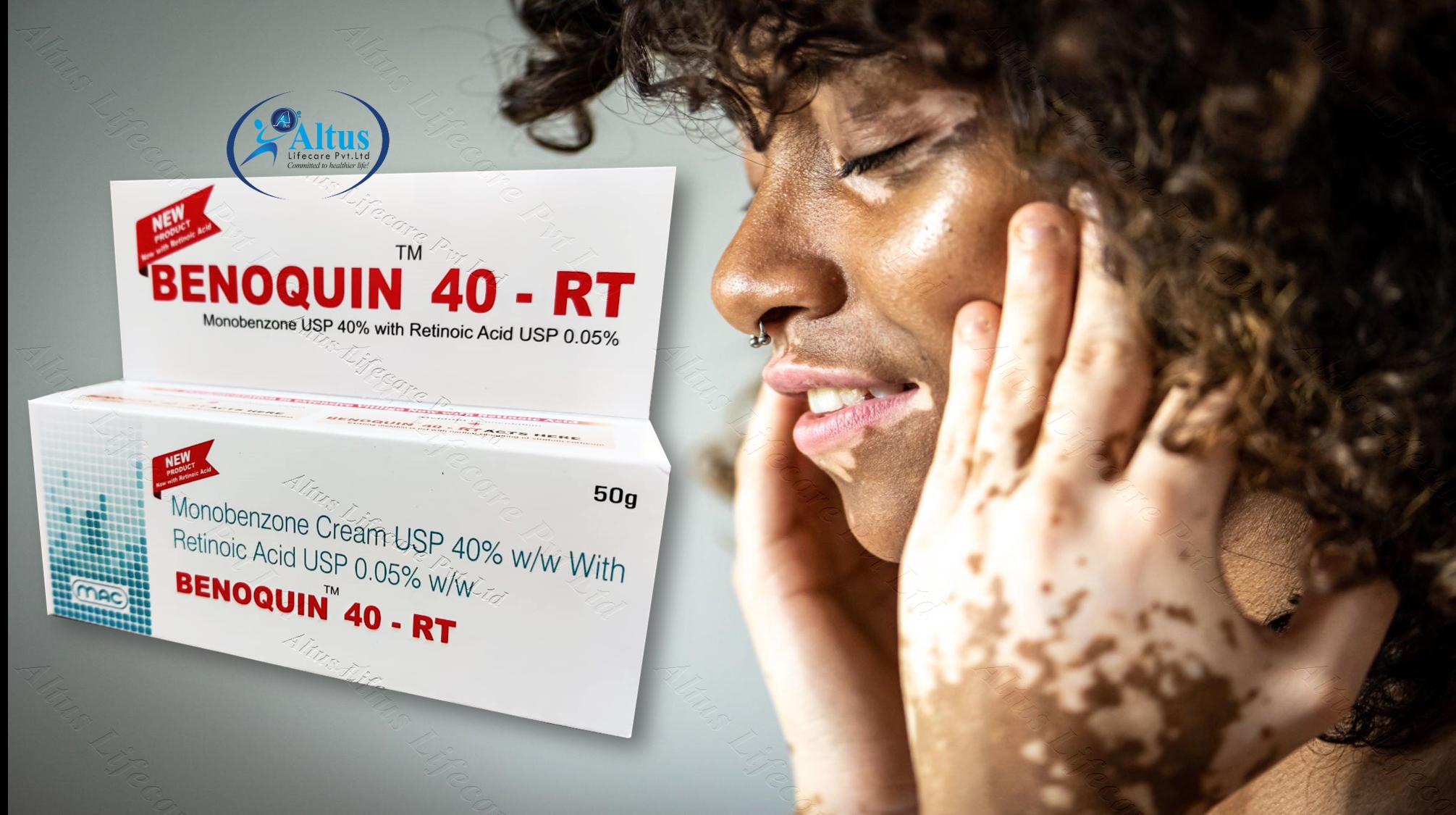
Benoquin 40 Jar | Monobenzone 40% Cream
| COUNTRY OF ORIGIN | India |
|---|---|
| DOSAGE FORM | Cream |
| EQUIVALENT BRAND | Benoquin 40% Jar |
| GENERIC NAME | Monobenzone |
| INDICATION | Vitiligo, lighten the skin |
| MANUFACTURER | Brinton Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd |
| PACKAGING | 100 gm in 1 jar |
| COMPOSITION | Monobenzone (40% w/w) |
| PACK SIZE | 3 Jar/s, 6 Jar/s, 9 Jar/s, 25 Jar/s |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
Benoquin 40 Jar is used for depigmentation. It is used to permanently lighten the skin in people with extensive vitiligo. It works by increasing the elimination of melanin from skin cells.
It is for external use only. You should always use it exactly as your doctor has told you. You must wash your hands thoroughly before and after applying this medicine. This medicine should be used regularly to get the most benefit from it. Do not use more than you need as some side effects may be increased.
It has a few potential side effects but not everyone will get them. These may include application site reactions like burning, irritation, itching, and redness. Serious allergic reaction to this drug is rare but let your doctor know if you’re bothered by side effects or they do not go away. Make sure you read the instructions that come with your medicine. Avoid contact with eyes. In case of accidental contact, you should rinse your eyes thoroughly with water.
You can start applying Jar to a small portion of unbroken skin or near the pigmented area for a period of several days for checking allergic reaction. You should discontinue it if itching, excessive inflammation, or swelling occurs. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should also consult their doctor before taking this medicine. If no improvement is seen after two months of treatment, the use of this product should be discontinued.
Benoquin and Skin Pigmentation: How It Works and What to Expect
Benoquin mechanism of action revolves around its active ingredient, monobenzone. Monobenzone decreases the melanin in the skin by inhibiting the activity of melanocytes, the cells responsible for melanin production. This lightens the skin in the depigmented areas, creating a more uniform complexion. However, it’s important to note that Benoquin should be used with caution, as it can lead to permanent depigmentation. It’s crucial for users to understand how the product works, what to expect during treatment, and the potential side effects associated with its use.
Depigmentation and Benoquin 40% Jar: How It Works and What to Know
It achieves its depigmentation effect primarily through its active ingredient, monobenzone. Monobenzone works by inhibiting the activity of melanocytes, the cells responsible for melanin production in the skin. As a result, the skin in depigmented areas becomes lighter. It’s important to note that the use should be approached with caution, as it has the potential to cause permanent depigmentation. Users should be well-informed about how the product works and understand the expected outcomes and potential side effects, which may include redness, itching, and dryness of the skin.
Skin Lightening with Monobenzone Cream: Mechanism and Considerations
Monobenzone cream operates by inhibiting the activity of melanocytes, the skin cells responsible for melanin production. This inhibition leads to a reduction in the skin’s pigmentation, resulting in a lighter appearance in the treated areas. While monobenzone cream can be effective for achieving skin lightening, it is essential to use it with caution and under professional guidance. Overuse or incorrect application can lead to undesirable outcomes, including uneven skin tone or permanent depigmentation. Understanding the cream’s mechanism and potential considerations is crucial for safe and effective use.
USES OF
- Vitiligo
BENEFITS
In Vitiligo
Vitiligo Treatment Options: Exploring Medical and Cosmetic Solutions
Managing vitiligo can involve a range of treatment options, both medical and cosmetic. Medical treatments include topical corticosteroids, narrowband ultraviolet B (NB-UVB) phototherapy, and excimer laser therapy, which aim to halt or slow down the progression of depigmentation. Cosmetic solutions, such as makeup and self-tanning products, offer individuals with vitiligo ways to conceal the depigmented areas temporarily. Surgical interventions, like skin grafting, may also be considered for some cases. The choice of treatment depends on the individual’s preferences, the extent of their condition, and consultation with a dermatologist.
Topical Vitiligo Creams: A Close Look at Treatment Options
Topical vitiligo creams are an essential component of the comprehensive treatment approach for vitiligo. These creams are designed to be applied directly to the depigmented skin areas. They may contain various active ingredients, such as corticosteroids or calcineurin inhibitors, which aim to promote repigmentation by suppressing the immune response or enhancing melanin production. The choice of topical vitiligo cream and the treatment plan should be tailored to the individual’s specific needs and the extent of their condition. Consulting with a dermatologist is crucial to select the most appropriate treatment option and develop a personalized plan.
SIDE EFFECTS OF JAR
Common side effects 
- Application site reactions (burning, irritation, itching and redness)
HOW TO USE JAR
HOW JAR WORKS
Medical Interventions for Vitiligo Treatment: What You Need to Know
Medical interventions play a crucial role in treating vitiligo. Dermatologists may recommend topical corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and promote repigmentation. Phototherapy, including narrowband ultraviolet B (NB-UVB) and excimer laser therapy, is another option. These treatments expose the skin to controlled UV light to stimulate melanin production. Medical interventions aim to halt the progression of depigmentation and potentially encourage repigmentation in the affected areas. Your dermatologist will guide you through the available options, helping you make informed decisions about the most suitable medical treatment for your specific case.
SAFETY ADVICE

Alcohol

Pregnancy
Breast feeding

Driving

Kidney

Liver